A lean business model canvas determines your business model in a visually descriptive way. In the same way as the original Business Model Canvas, this ‘lean’ version, ideal for startups, will help you construct your business plan more efficiently and help draft a business model for your idea or business.
We talked in our last article about how to construct a business plan and what needs to go in it. But, a lean business model canvas can be built quicker. A lean business model canvas is perfect for startups as it is all about getting ideas down quickly. You then use it as a starting point to test assumptions and align the founders’ direction. It is essential to be able to demonstrate your business model clearly to get colleagues, fellow founders, investors and partners on board with a specific direction. Our team founders, like all entrepreneurship teams, can find this method tricky the first time they do it. It’s merely another one of those learning curves on the way to startup success. The lean business model canvas course is just one of the entrepreneurship training exercises that our teams go through to ensure their future success. Alacrity is an entrepreneurship educational 15-month course where we educate you, fund you and give you the skills to grow (we also pay you on the course). to apply or for more information click here > Our entrepreneurs here at Alacrity get taught first-hand about business planning and what needs to be included to convince investors. This is because our 15-month course concludes in an investment round!FIND OUT MORE ABOUT OUR 15-MONTH PAID ENTREPRENEURSHIP COURSE THAT TAKES GRADUATES, BUILDS TEAMS AND THEN INVESTS IN THE NEW COMPANIES >
In 2008, Osterwalder’s original business model canvas was formed. This business model canvas is ideally printed out as big as possible, or written on a large whiteboard so that your whole team can work on it. Ideas can be added, subtracted, and moved around as you work towards a more precise business model for your startup. Following the original business model canvas came several iterations specific to business needs. Here we’re going to talk about the ideal one for entrepreneurs and startups, the Lean Business Model Canvas. The Lean Business Model Canvas is more straightforward and less comprehensive than the original Business Model Canvas. The Business Model Canvas aims to provide a complete model of a business based on larger corporation thinking (like Skype or Apple). The Lean Canvas has a more creative approach based on timelines, revenue streams and targets. This has also become more focused as it is shorter and achieves a simpler business model. The Lean Canvas is more suited to entrepreneurs and startups as it is more actionable by focussing on factors such as uncertainty and risk.
The Lean Business Model Canvas Framework
Like the original canvas, the lean business model canvas framework also contains nine sections. Let’s dive into each one.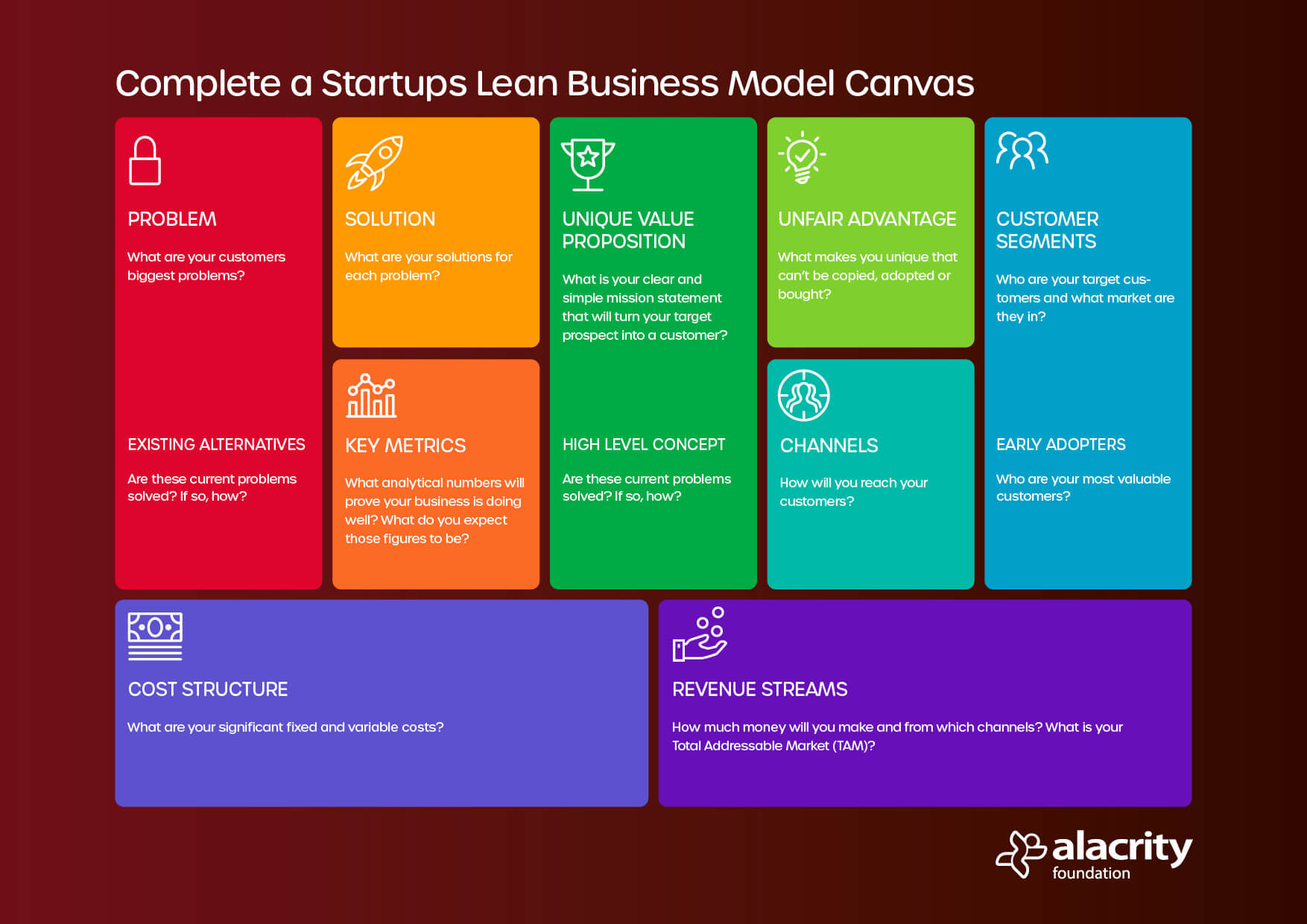
Problem
The problem is first addressed. Without identifying and realising the problem, businesses will fail to apply effort, adequate resources and time in building the right product. It is, therefore, vital to understand the problem in the first instance. What problem do users have that your idea or business will correct? Also, in the problem, you should identify alternatives available to solve this problem. Again, this can be as simple as using Excel and Word. Trying to change peoples habits is the hardest thing to do in business! Forming and identifying a fundamental problem will help ensure that you are meeting a pre-existing industry need and start you on the path towards identifying solutions.Solution
You’ve identified your problem, recognised alternatives and workarounds and now you need to be specific about your answer. The solution here will visualise in bullet form what your MVP (Minimum Viable Product) will contain. What are the features and outcomes that will be obtained from version 1.0 of your product? This box is half the size of the problem section as it needs to be laser-focused in its ability and simplicity in solving the problem.Key Metrics
In the same way as marketing campaigns are run, identifiable key metrics need to identify what success looks like. Startups can better build a business around less key metrics and focus on one or two identifiers. For instance, our Alacrity teams have used different parameters depending on their area of business. An achievable percentage of subscriptions during their first quarter, or the GMV (Gross Merchandise Value) that goes through a platform as well as visits to the website with an anticipated conversion rate of 2%. All are valid key metrics and may need tweaking due to your initial assumptions. From experience, whatever you propose as achievable key metrics; halve them and still ensure your lean business model balances well.Unique Value Proposition (UVP) or Unique Selling Point (USP)
Here, written in simple to understand language, is your mission statement and promise to your target market that your solution solves their problem. Positive, reactive words need to be adopted to create excitement with your idea. For instance, CulturVate has a UVP:“We enable companies to retain and reward employees keeping them engaged while socially collecting their innovative ideas”.Identify things like the value that you bring your customers along with the problem that you solve. What differentiates you from your competition and what’s different and fresh about you as a startup that can achieve this ambition? This box also includes an even simpler area to identify an A for B analogy. For instance, Culturvate would be
“LinkedIn for Ideas”.
Unfair Advantage
This should list your competitive advantage. A startup needs to identify whether or not it has something than can be easily copied, adopted or bought.Channels
Here you need to identify your channels to market. After all, your company won’t survive if you don’t reach customers who want to purchase your product, so how will you reach them? You could serve customers directly through an outbound, phone call and email-driven approach, or you could decide to use partner channels like Amazon, SalesForce or Mitel.Customer Segments
Your business is not going to survive without customers, so it is essential to identify and determine what your customer segments are. This lean business model canvas should focus on one of the five specific customer segments. These segments are:- Mass Market – Your business appeals to the broadest possible range of people.
- Niche Market – Your business appeals to a specific group of customers with particular needs.
- Segmented – These are multiple markets within your primary market. You may need to segment further based on demographics like age, gender, or location.
- Diversified – You serve more than one market segment.
- Multi-Sided Platform – Platforms that serve two markets simultaneously, for instance, you could be a go-between for business and consumers like an HR platform similar to SumoShift.


The template you show here, where can I download it?
Click on the image above, otherwise, the direct link is here…
https://alacrityfoundation.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Lean-Business-Model-Canvas-Coloured.pdf